Momentum Only Grows
Industry-wide, cloud computing has revolutionized the way enterprises manage, scale, and process large-scale applications, and derive value from data. The International Data Corporation (IDC) forecasts that the worldwide public cloud services and infrastructure spending will reach $1 trillion in 2024 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7%.
Amid globalization and the growing demands of a remote workforce, companies of all sizes have now moved to cloud environments. Cloud technologies leverage a shared IT infrastructure and a reliable internet connection to enable users to manage multiple apps, solve workload challenges, and significantly reduce the company’s computing costs.
The elasticity of the cloud (the ease of growing or shrinking your platform-use as needs change) and its flexibility (on-demand availability, high efficiency, and advanced IT capabilities) means it is no longer seen as just an online data back-up server. Nothing short of a revolution is happening, now – cloud is ubiquitously accepted as a powerful and necessary tool required for a business to evolve and adapt.
Let’s take a deep dive into cloud computing, its advantages, and why you should consider embracing this paradigm shift.
Connect with Trianz for Cloud Benchmarking Services
"Cloud-first strategies are your business’s key to constant adaptability in a continually advancing business landscape, guaranteeing longevity and growth well into the future."
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud technology enables the reusability of IT resources for storing large databases, developing and hosting complex applications, and expanding computational power and other services on demand. Eliminating or reducing investments in large-scale infrastructure and software, coupled with the pay-per-use model, significantly reduces IT costs.
Here are some traditional computing techniques that have helped enterprises achieve additional computing and storage capabilities:
- Cluster computing connects different computers in one location via LAN to work as a single computer, improving the combined performance of the organization.
- Grid computing enables collaboration between enterprises to carry out distributed computing jobs using interconnected computers spread across multiple locations running independently.
- Utility computing provides web services such as computing, storage space, and applications to users at a low cost through the virtualization of several backend servers.
- Distributed computing landscapes connect ubiquitous networks and connected devices, enabling peer-to-peer computing. Examples of such cloud infrastructure are ATMs and intranets/workgroups.
History of Cloud Computing
The abstract idea of cloud computing developed when mainframe computers were primarily used to access applications and data residing on clients’ localized infrastructure.
We saw the birth of IT services coupled with a growing demand for personal computers using decentralized computing resources.
With the dot-com revolution, industries adopted dynamic client/server architectures with service providers’ offering virtual private networks.
The outsourcing of IT infrastructure management began when companies needed the capabilities to provide advanced server virtualization services via hosted cloud environments.
Cloud computing evolved to incorporate the delivery of cloud deployment models including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
Cloud collaboration — a hybrid collection of enterprise applications and virtualized social interaction tools — is offered as a service that allows multiple users to work together simultaneously on a particular task.
Who Uses the Cloud and Why?
Cloud’s evolving features are changing the way organizations of every type, size, and industry manage and process data. This includes everything from utilizing unlimited storage; adopting powerful analytics tools; updating applications and system infrastructure software; strategizing customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource management (ERM); and migrating content and collaborative applications, as well as data management and delivery applications.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud computing offers on-demand delivery of digital resources, allowing organizations and individuals the flexibility to eliminate or reduce legacy data applications and infrastructure. With pay-as-you-go cloud services, users only pay for their hardware and software consumption. With cloud computing, organizations are becoming more agile, reducing cost, innovating faster, and transforming their business goals and objectives with powerful analytics tools.
Types of cloud computing services

IaaS
IaaS is a cloud computing model where virtualized infrastructure is offered to and managed for businesses by external cloud providers. With IaaS, companies can outsource for storage, servers, data center space, and cloud networking components connected through the internet, offering similar functionality as that of on-premises infrastructure.
Examples of IaaS are automated, policy-driven operations such as backup, recovery, monitoring, clustering, internal networking, and website hosting. The service provider is responsible for building the servers and storage, networking firewalls/ security, and the physical data center.
Key players offering IaaS are Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), GoGrid, Rackspace, DigitalOcean among others.
PaaS
PaaS builds on IaaS. With PaaS, cloud vendors deliver cloud software and hardware infrastructure components like middleware and operating systems that are required to develop and test applications. The PaaS environment enables users to install and host data sets, development tools, and business analytics applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure.
Key players offering PaaS are Bluemix, CloudBees, Salesforce.com, Google App Engine, Heroku, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, OpenShift, Oracle Cloud and SAP.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is unique in that it incorporates both IaaS and PaaS. With SaaS, the cloud service provider delivers the entire software suite as a pay-per-use model. SaaS allows users to easily access software applications such as emails via the internet.
The most well-known SaaS applications are Microsoft Office 360, AppDynamics, Adobe Creative Cloud, Google G Suite, Zoho, Salesforce, Marketo, Oracle CRM, Pardot Marketing Automation, and SAP Business ByDesign.
Public Cloud
The public cloud is the most economical option for users because the service provider bears the expenses of bandwidth and infrastructure. It has limited configurations, and the cost is determined by usage capacity. Despite the public cloud’s having high reliability, lower costs, zero maintenance, and on-demand scalability, it is not suitable for organizations operating with sensitive data and strict security regulations.
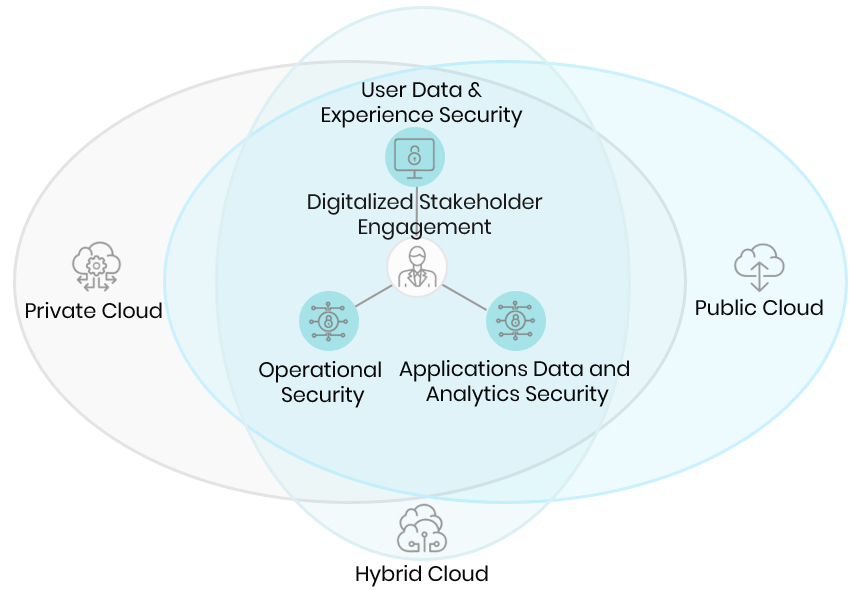
Private Cloud
The private cloud provides more control over customizability, scalability, and flexibility, all while improving security of assets and business operations. Private cloud infrastructure can be built on-premises or outsourced to a third-party service provider. Its main advantage over the public cloud is its ability to maintain the hardware and software environment over a private network exclusively for the owner. Large- and medium-scale financial enterprises, as well as government agencies, typically opt for private clouds.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds are the combination of a private and public cloud. This provides more flexibility by allowing businesses to have control over critical operations and assets. The hybrid cloud architecture enables companies to manage private and public clouds through one portal and optimize workloads for each environment's strengths. For example, businesses can use the public cloud for running high-volume applications like emails and utilize private clouds for sensitive assets like financials, as well as data recovery – plus eliminating downtime during scheduled maintenance.
10 Benefits of Cloud Computing
Scalability
Cloud computing enables immediate scalability of infrastructure capacity depending on the business need. Data storage capacity, processing power, and networking can all be scaled up or down quickly and easily with little to no disruption or downtime.
Accessibility
Cloud computing empowers enterprises to deploy their applications across the globe to provide service to their customers whenever and wherever it is needed. This allows customers to get an identical digital experience unhindered by geographic limitations.
Operational Agility
Businesses must have the ability to instantly scale their cloud capacity by accessing bandwidth demands from remote servers. If the business demand is increased, the enterprise can turn up its computing capacity and IT resources availability instantly. This resulting operational agility improves productivity, efficiency, and innovation, and it offers a competitive advantage and opportunity for disruption.
Reduced Expenditure
With the cloud, enterprises can focus on building their business rather than investing in hardware infrastructure and data centers that either remain idle or underutilized. As mentioned before, public cloud costs depend on consumption and remain a variable expense.
Automatic Updates/Patches
When enterprises deal with various software, operating systems, and applications from different vendors they require software and security updates to be performed on a regular basis. This can be a time-consuming process, and the downtime for system maintenance means loss of productivity. A cloud service provider or a managed service provider can take care of these automatically, saving time and manual effort on maintenance.
Read our report offering data-driven insights – drawn from 9,000+ responses and 5,000+ companies - on the state of transformations by industry, geography, business and technology function.
Disaster Recovery
Deploying robust cloud backup and disaster recovery plans are crucial for business continuity. Traditional on-prem backup and recovery solutions are time-consuming to maintain and do not always offer full recovery in the event of a major disruption. Cloud-based disaster recovery allows for quicker recovery of data and applications and minimizes downtime and data loss.
High Security
Protecting sensitive, personally identifiable and/or financial information is a considerable challenge for CIOs. Advanced cloud security features, however, reduce the risks of information loss and cyber stealth.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
In comparison to traditional on-prem servers, cloud infrastructure significantly reduces energy usage, IT infrastructure, and consumption by offering resources as-per-demand, thereby reducing e-waste and its adverse impact on the environment.
Flexibility
The cloud allows anyone to launch new products and services from anywhere with ease. Furthermore, being free of regulation imposed by third-party IT providers and unnecessary financial commitment improves business flexibility and agility.
Enterprise Collaboration
Apart from those using the enhanced security measures of private clouds, company information no longer exists in silos. Centralized documentation control on cloud-based, file-sharing, and social communication apps offers transparency and visibility into work processes, streamlining information flow and better enabling collaboration between teams, departments, and employees seated in different time zones — all of which leads to improved productivity and bottom line.
Benefits of a Cloud-hosted CRM
CRM software on the cloud enables business teams to access accurate and consistent customer information. CRM stores customer details like names, contact numbers, and addresses, while tracking customer activity such as website visits, phone calls, and emails. Cloud-hosted CRM offers a competitive advantage to enterprises by helping them manage interactions with their clients and prospects.
With cloud-hosted CRM, businesses of all sizes can afford a variety of user-friendly CRM solutions to build better customer relationships. CRM’s hassle-free installation, 24/7 availability, reliability, high security, scalability, and easy-to-use features allow easy access for businesses to provide better service to their clients. Cloud CRMs are also compatible with multivendor products and applications that elevate their operational effectiveness.
Taking the First Step
Rapidly changing customer demands are forcing businesses to adopt the cloud or risk obsolescence. Here are the recommended steps organizations should follow in their cloud adoption process:
Assess the challenges, opportunities, business value, and feasibility of the migration planning.
Formulate and standardize a roadmap with suitable deployment models and architectures.
Develop cloud migration strategies and methodologies for adoption.
Optimize and refine the business processes and deployments to increase efficiency and impact.
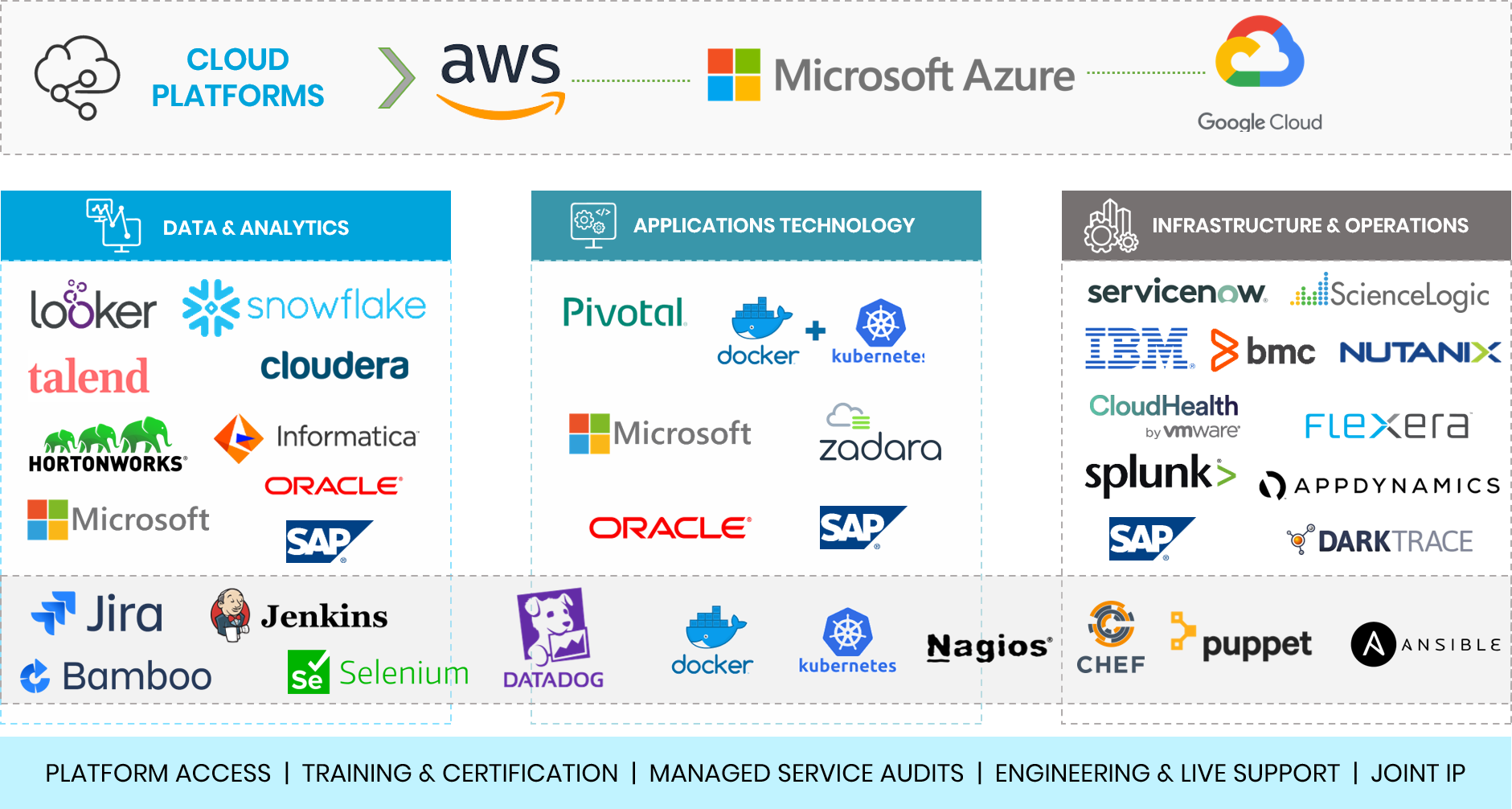
Some of the most powerful cloud services providers (CSPs) in the industry today are:
AWS Cloud
AWS is the most dominant cloud vendor offering comprehensive IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services. AWS’ key portfolio includes:
- Compute (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud – EC2)
- Storage (Amazon Simple Storage Service – S3)
- Data management (Amazon Relational Database Service – RDS), Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Redshift)
- Hybrid cloud (AWS Migration Hub)
- Networking (Amazon Virtual Private Cloud – VPC, AWS Direct Connect)
- App development tools (AWS Command Line Interface, AWS CodeCommit, AWS Step Functions, Amazon Elastic Transcoder, Amazon API Gateway)
- Infrastructure management (Amazon CloudWatch, AWS OpsWorks, AWS CloudFormation, AWS Trusted Advisor, AWS Config)
- Analytics (Amazon QuickSight, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon EMR)
- Governance and Security (AWS IAM, Amazon Inspector, AWS Organizations, AWS CloudTrail)
- AI and Machine learning (Alexa Skills Kit, Alexa Voice Services – AVS, Amazon Lex, Amazon SageMaker, AWS DeepLens)
- AWS IoT
- Amazon AppStream 2.0
- Mobile apps (Amazon Pinpoint, Amazon Cognito, and AWS Mobile Hub) and document, data management, and email services
Microsoft Azure
Azure offers DevOps, integrated tools, and serverless computing support to IT professionals globally, enabling them to build and manage both web and mobile applications and solutions. Azure is configured to develop open-source software, mobile platforms, multiple operating systems and programming languages, devices, databases, and frameworks.
Azure’s on-premises and hybrid cloud models provide maximum security and ease of management for application development. Its built-in AI enables the development of data-driven, intelligent apps that create new user experiences based on real-time analytics.
GCP
GCP provides a suite of public and private-hosted cloud services for machine learning, big data analytics, app development, storage, networking, software development, security, and other computational infrastructure to companies globally.
Its services include IaaS (Cloud Engine), PaaS (Google App Engine), Google Cloud Storage and Google Container Engine (Dockers), big data processing (Google Cloud Dataproc), Google Cloud IoT Core, and AI Cloud Machine Learning Engine, as well as many others.
Oracle Cloud
This offers enterprise-grade IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud services through its data centers. Oracle has a wide range of integrated digital solutions, including intelligent business applications, platforms, storage networks, servers, and data offered as a service. With Oracle Cloud, businesses can focus on delivering customer-centricity, analyze trends and customer behavior, take advantage of new and evolving market opportunities, and reap the benefits of advanced security and data protection.
Salesforce
Salesforce’s CRM is a cloud software that empowers businesses with automation. Apart from streamlining business processes, it also allows better management and execution of sales and marketing strategies in addition to customer service activities.
IBM Cloud (Formerly Bluemix and SoftLayer)
IBM is one of the prominent players in the IaaS and PaaS marketplace. IBM’s services and solutions include computing, networking, storage, cloud deployment management, data management, security, analytics, AI, mobile tools, VMware, blockchain, and developer tools to build apps.
One thing is clear: Cloud computing will continue to evolve. Organizations need a technology partner that is well-versed with the market, accurately understands the technology requirements of its clients, and takes pride in helping them achieve their long-term business objectives.
How to Choose a Cloud Provider
Some CIOs may lack the necessary knowledge or guidance to choose a cloud partner equipped to help them achieve their business goals. Before committing to a cloud vendor, it is essential for companies to understand the provider’s services, the pricing model, security and safety parameters, data center location(s), data recovery options, customer support capabilities, scalability, operational outages scenarios, deployment, user-friendliness, and accessibility.
As a preferred cloud consulting partner working with major CSPs including AWS, Microsoft Azure, GCP, Oracle Cloud, and Salesforce, Trianz provides a holistic view of cloud technologies to help clients gain optimal value from their cloud migrations. With proven cloud migration frameworks, roadmaps, and deployment expertise, Trianz transforms organizations of all sizes into efficient digital enterprises.
Experience the Trianz Difference
Trianz enables digital transformations through effective strategies and excellence in execution. Collaborating with business and technology leaders, we help formulate and execute operational strategies to achieve intended business outcomes by bringing best-in-class consulting services, technology expertise, and execution models.
Powered by knowledge, research, and perspectives, we enable clients to transform their business ecosystems and achieve superior performance by leveraging infrastructure, cloud, analytics, digital, and security paradigms. Reach out to get in touch or learn more.


